Zebrafish are model organisms for biomedical research. There are structural, functional, and genetic similarities with humans that make zebrafish a useful model for not only cardiovascular research but also oncology, developmental biology and aquaculture. Zebrafish are small, develop quickly, and because they are vertebrates, they share many of the same organs and cell types as mammals.
Benefits of Vevo imaging across applications:
Cardiovascular
Oncology
Developmental
- High-throughput cardiovascular phenotyping
- Systolic and diastolic function
- Advanced speckle tracking and strain analysis
- Tumour detection and sizing superior to visual inspection
- From the earliest stages
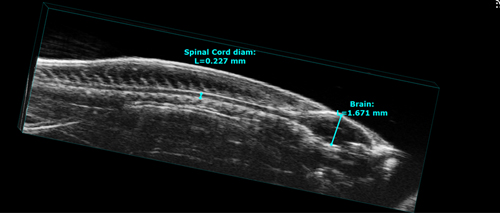 Above: High frequency ultrasound of the central nervous system of a zebrafish.
Above: High frequency ultrasound of the central nervous system of a zebrafish.
Benefits of Vevo high frequency ultrasound for imaging zebrafish:
- Imaging unaffected by skin pigments
- Fish imaged in natural environment
- High frame rates
- Precise assessment of blood flow and heart rate
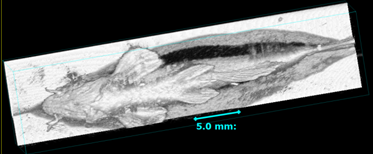
Above: Whole body scan of an adult zebrafish under tricain anesthesia. Image positioning for zebrafish cardiac phenotyping. Note the zebrafish is lying in a groove to remain in a stable position.