Acquire Robust Data to Support Your Colorectal Cancer Research
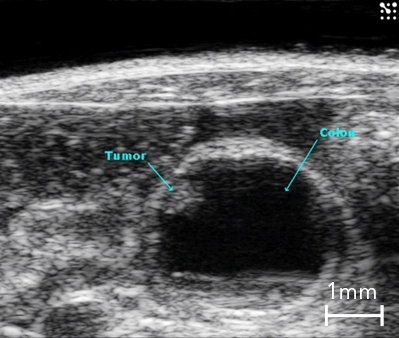
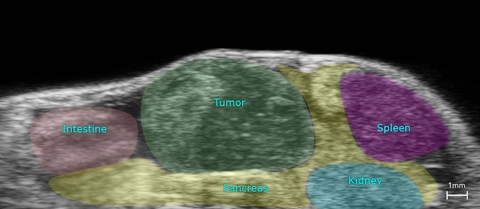
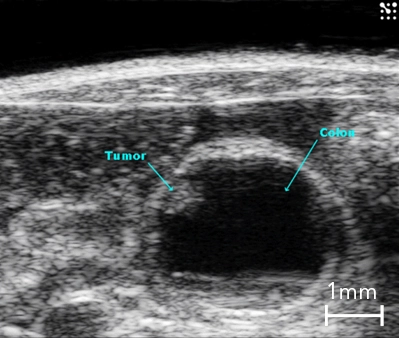
B-Mode image of the mouse colon with tumor highlighted.
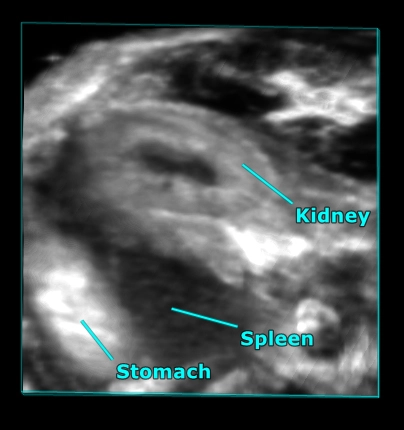
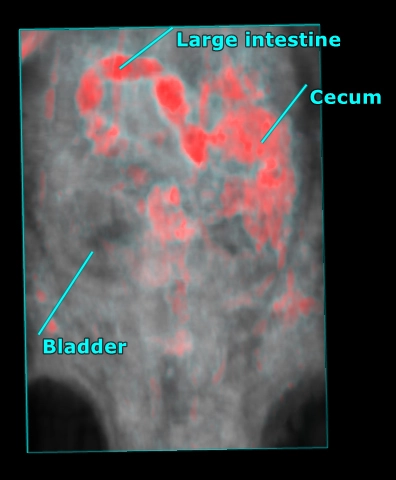
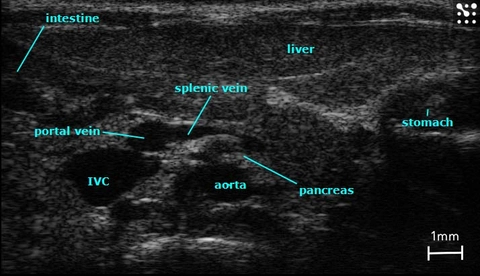
With the Vevo Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) imaging systems you can delineate colon walls, abnormalities, and tumors with high resolution.
How Can Ultra-High Frequency Ultrasound Help with GI research?
- Non-invasive, pre-palpable tumor identification
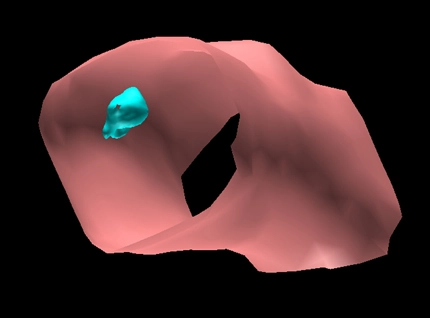
- 3D volume quantification
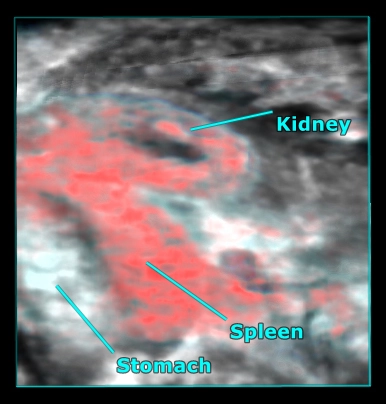
- Contrast-enhanced imaging colon and tumor perfusion
- Intestinal motility and inflammation models
RECORDED WEBINAR
Assessment of Murine Colorectal Cancer by UHF Ultrasound using 3D Reconstruction and Non-Linear Contrast Imaging
Presented by Jessica Freeling, MS, VT, LATG, Physiology Core Laboratory Manager, The University of South Dakota
Includes:
• Colorectal cancer (CRC) background information
• Common CRC Mouse Models
• Imaging Modalities and Limitations
Publications
TOP PAPER
A Novel Noninvasive Method for Quantitative Detection of Colonic Dysmotility Using Real-Time Ultrasonography
Digestion
,
TOP PAPER
Molecular Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging of Radiation-Induced P-Selectin Expression in Healthy Mice Colon
International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics
,
TOP PAPER
Assessment of murine colorectal cancer by micro-ultrasound using three dimensional reconstruction and non-linear contrast imaging
Molecular Therapy — Methods & Clinical Development
,
TOP PAPER
In-vivo monitoring of acute DSS-Colitis using Colonoscopy, high resolution Ultrasound and bench-top Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Mice
European Radiology
,
TOP PAPER
Role of innate immunity and altered intestinal motility in LPS- and MnCl2-induced intestinal intussusception in mice.
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology
,
TOP PAPER
High-frequency ultrasound for in vivo measurement of colon wall thickness in mice.
Ultrasound in medicine & biology
,
TOP PAPER
Intraluminal gel ultrasound and eco-color doppler: new tools for the study of colorectal cancer in mice.
In vivo (Athens, Greece)
,
TOP PAPER
Assessment and Monitoring Tumor Vascularity With Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Maximum Intensity Persistence Imaging
Investigative Radiology
,
TOP PAPER
Anti-VEGF therapy reduces intestinal inflammation in Endoglin heterozygous mice subjected to experimental colitis
Angiogenesis
, Request a Quote or Demo